NooJ
A Corpus Processor - A Linguistic Development Environment - A Linguistic Engine for developing Natural Language Processing software Applications.

A Corpus Processor
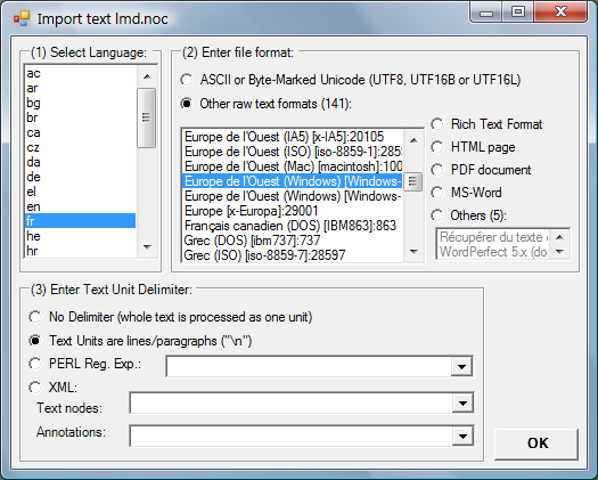
Import text files in any format
Construct your own corpus by importing text files in 150+ file formats. Texts can be structured (e.g. XML).
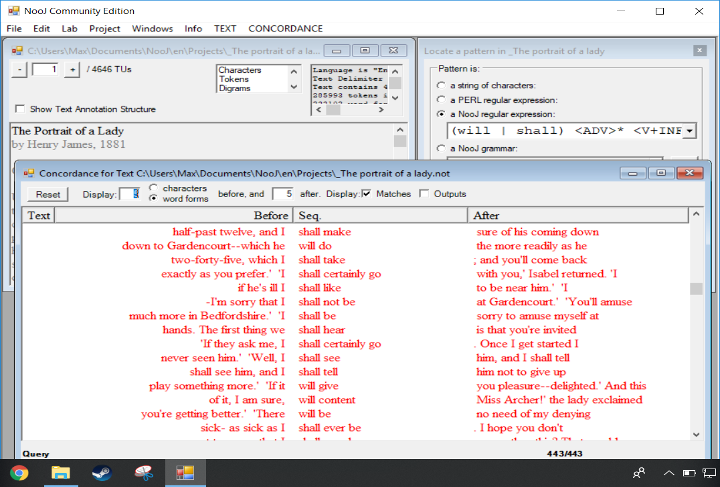
Apply a query
Enter a regular expression to produce the corresponding concordance. The regular expression here:
(will | shall) <ADV>* <V+INF>
recognizes sentences that contain a verb in the Future tense.
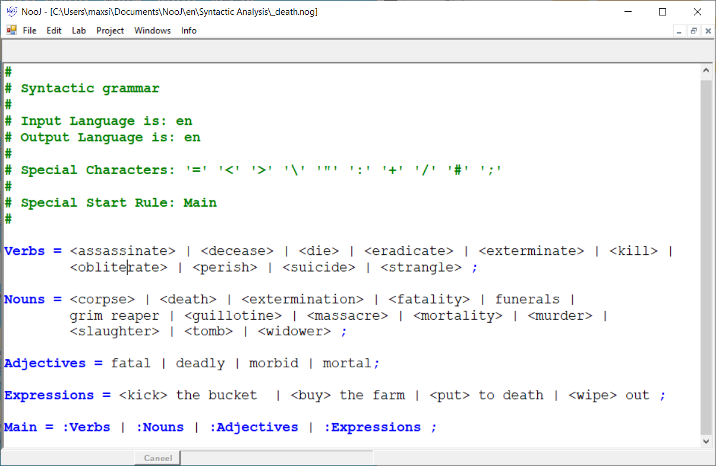
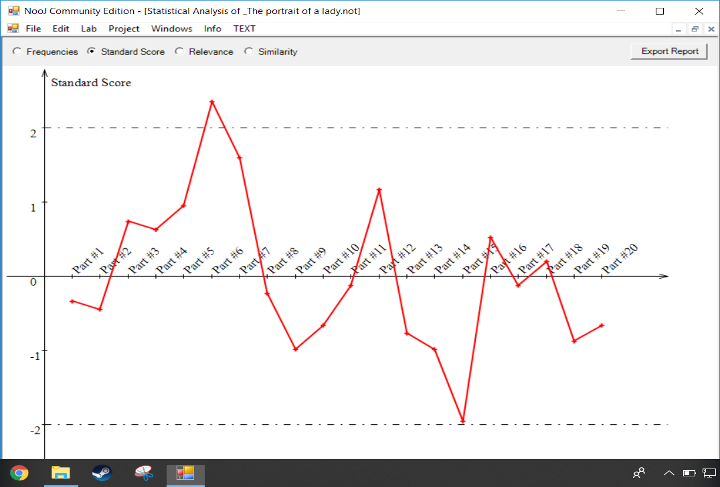
A lexical field
Define and accumulate lexical fields via NooJ grammars (here: "death" theme) and apply them automatically to index and color texts, construct concordances, perform statistical analyses, etc.
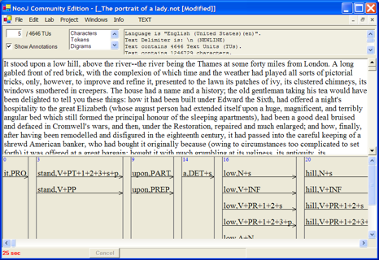
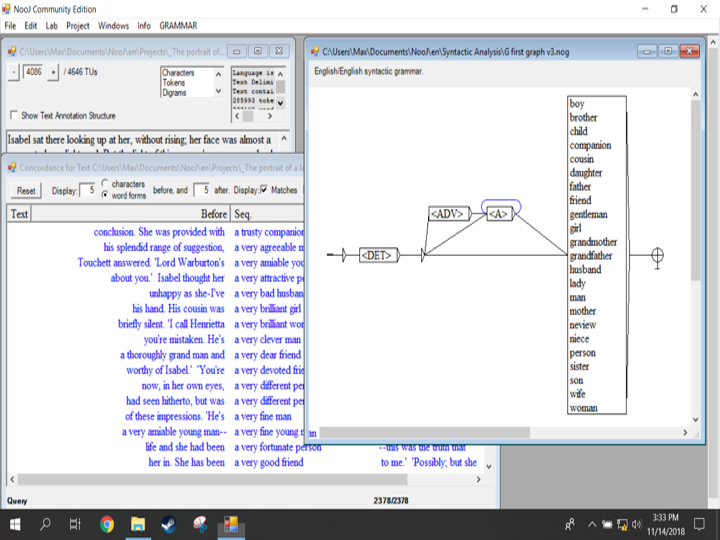
Text Annotation Structure
All linguistic analyses' results are stored in the TAS. Linguistic resources are used to add and/or remove annotations to the TAS. TAS can be imported from or exported to XML files.
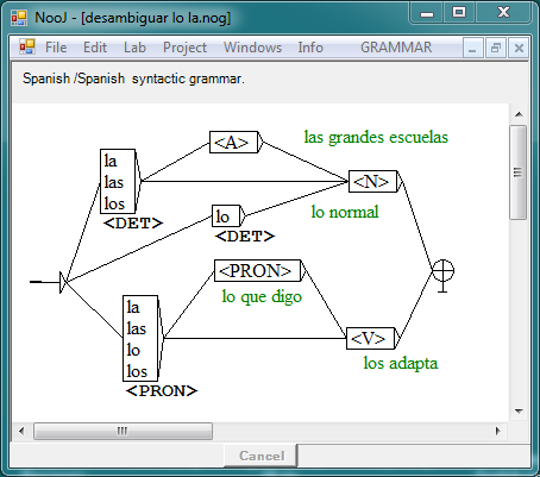
Automatic Disambiguation
Local grammars can be used to remove ambiguities. The Spanish word "la" is disambiguated as a pronoun or a determiner, depending on its right context.
Linguistic Engineering
NooJ contains a dozen tools to help develop and edit, test, debug, check consistency of all linguistic resources. Here: the grammar's contract garantees the grammar's consistency.
Develop Linguistic Resources
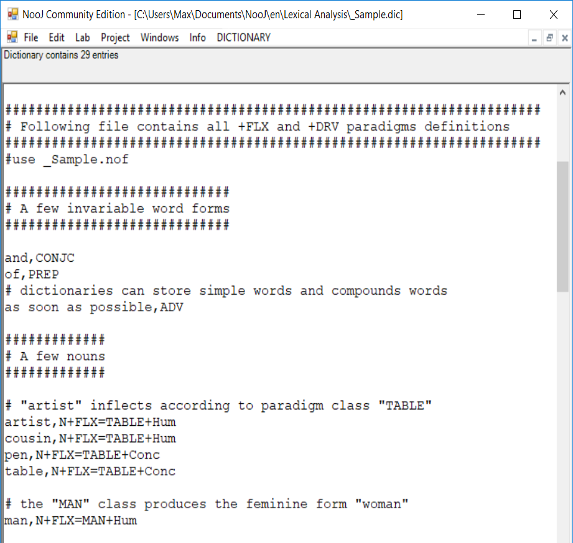
Dictionaries
NooJ's dictionaries manage any type of Atomic Linguistic Units (ALUs): simple words, multiword units, intra-word units as well as discontiguous expressions.
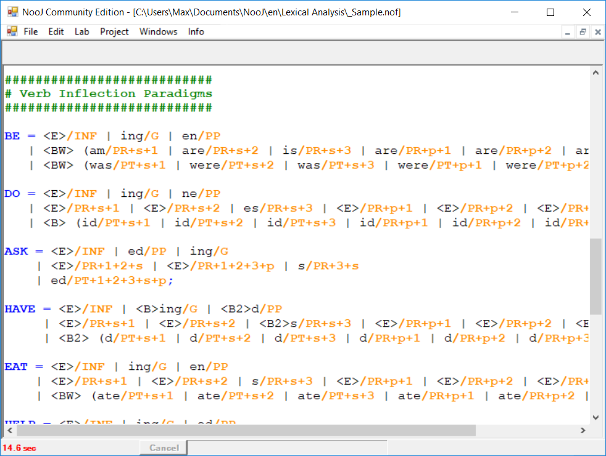
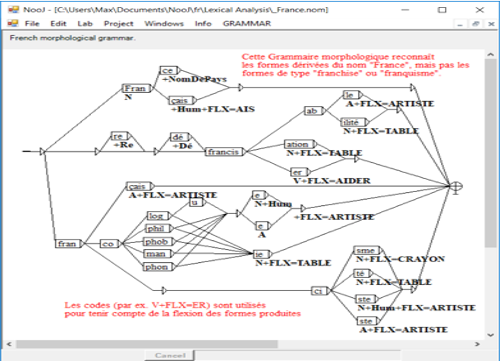
Inflection and Derivation
Inflectional and Derivational paradigms can be formalized with enhanced regular or Context-Free rules.
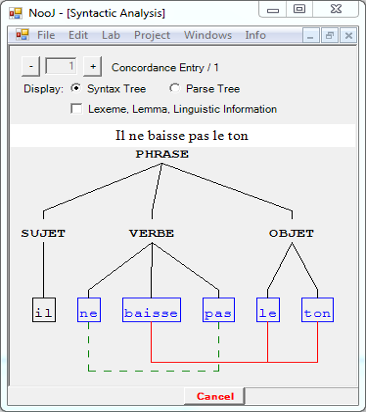
Syntactic Trees
NooJ can display Derivation, Constituent and Dependency Trees, taking into account all types of ALUs. The text here contains two discontiguous ALUs: "ne ... pas" (French negation) and "baisser ... le ton" (French idiomatic expression).
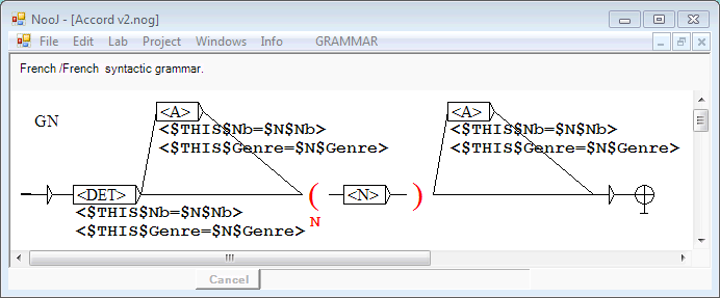
Context-Sensitive Grammars
NooJ grammars can include various types of linguistic constraints existence, distributional restrictions, agreements, etc. The grammar here verifies agreement in Gender and in Number among all components of a French Noun Phrase.
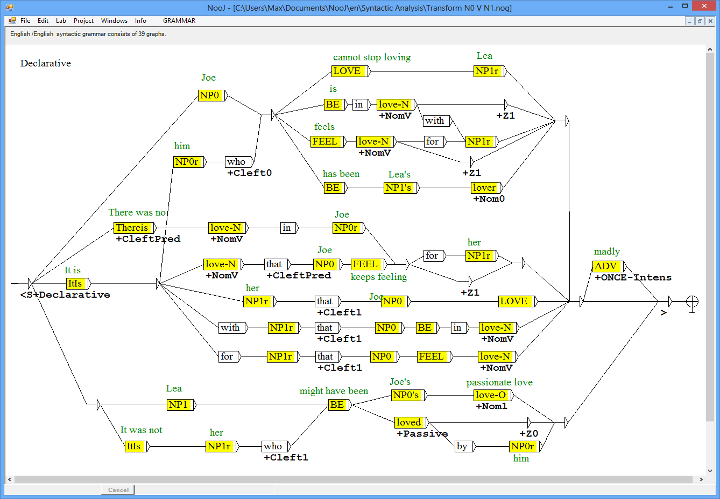
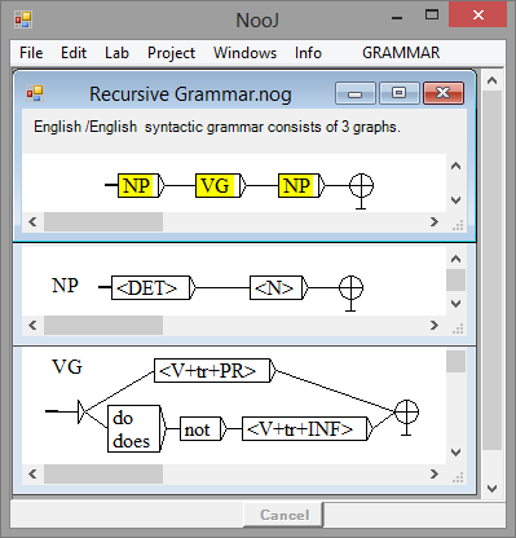
Unrestricted Grammars
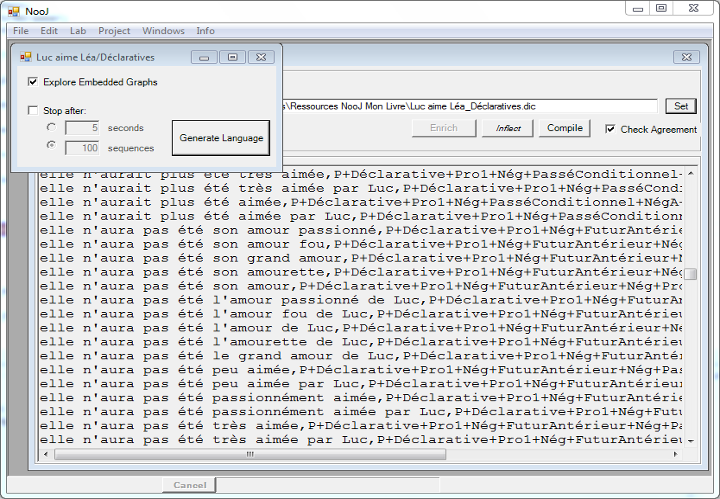
Unrestricted grammars allow NooJ to link syntactic and semantic variants, such as a noun and its pronoun, a verb and its nominalized form, etc. The grammar here represents all variants of a simple transitive sentence such as "Joe loves Lea', including aspects, modality, nominalizations, focus, pronouns, tense, etc.
Over a dozen Natural Language Processing Software Applications
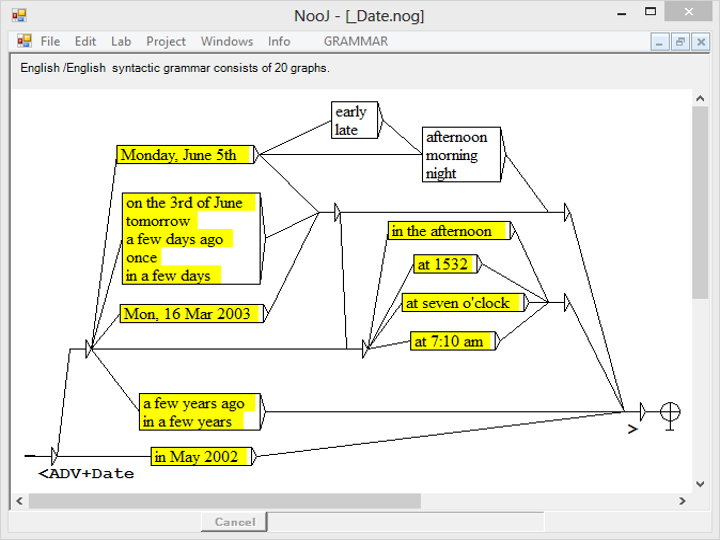
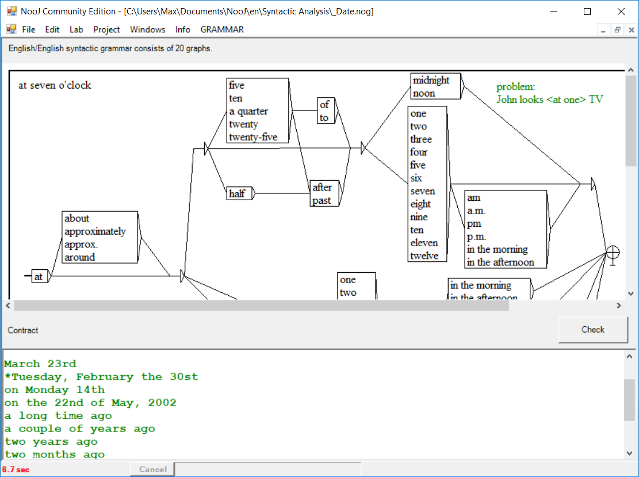
Named Entity Recognition
NooJ has been used to develop NERs in over 20 languages. The graph here is part of a 20-graph grammar used to recognize and annotate English dates automatically.
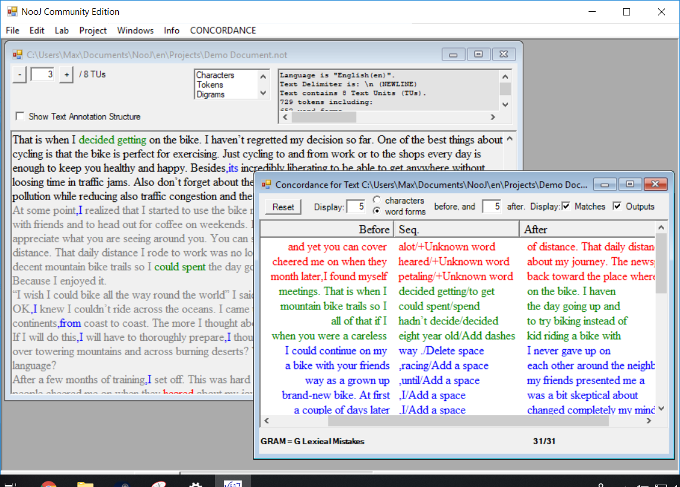
Grammatical Checker
Local grammars can be developed to recognize and annotate specific grammatical mistakes.
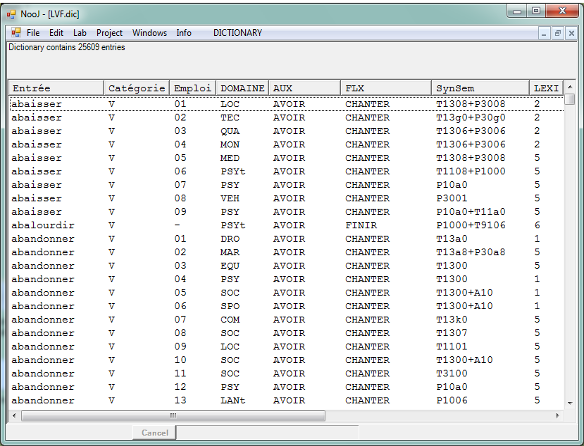
Semantic Disambiguation
NooJ manages lexicon-grammars as well as semantic dictionaries. Here, the LVF dictionary (Dubois & Dubois-Charlier 1997) contains 25,000 different verb meaning, associated with their characteristic syntactic and semantic contexts.

Intelligent Search Engine
By applying the LVF dictionary to one's corpus of texts, it becomes possible to pinpoint a specific meaning of a verb. Here NooJ has found in the newspaper Le Monde Diplomatique, 2002, all occurrences of the verb abriter, sense #4: to hide oneself behind a pretext in order not to act.
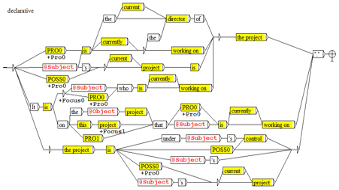
Semantic Analysis: Text to RDF to Text
NooJ grammars can be used to parse texts in Natural Languages and produce a semantic representation (e.g. in RDF), and reciprocally: produce all the sentences that can express a predicate represented by an RDF statement.
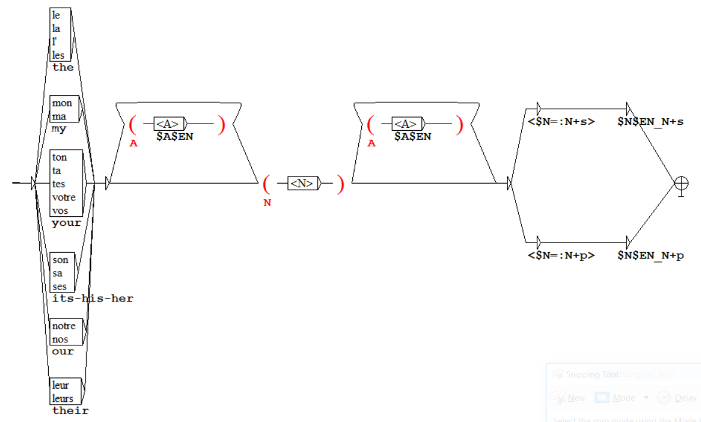
Machine Translation
NooJ is being used to develop automatic translation systems: Arabic to French, Arabic to English, Portuguese to English, Greek to Spanish, etc. Here, a simple grammar recognizes some French NPs and translate them in English, reordering the adjectives and taking Number agreement into account.